Product Description and Product Data
This is an all-inclusive cell-based luciferase reporter assay kit targeting the Human Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain enhancer of activated B cells (NF-kB). INDIGO’s NF-kB reporter assay utilizes proprietary mammalian cells that have been engineered to provide constitutive expression of NF-kB. In addition to NF-kB Reporter Cells, this kit provides two optimized media for use during cell culture and in diluting the user’s test samples, a reference agonist, Luciferase Detection Reagent, and a cell culture-ready assay plate. The principal application of this assay is in the screening of test samples to quantify any functional activity, either agonist or antagonist, that they may exert against human NF-kB. This kit provides researchers with clear, reproducible results, exceptional cell viability post-thaw, and consistent results lot to lot. Kits must be stored at -80C. Do not store in liquid nitrogen. Note: reporter cells cannot be refrozen or maintained in extended culture.
Features
Clear, Reproducible Results
- All-Inclusive Assay Systems
- Exceptional Cell Viability Post-Thaw
- Consistent Results Lot to Lot
Product Specifications
| Target Type | Transcription Factor | ||
| Species | Human | ||
| Receptor Form | Native | ||
| Assay Mode | Agonist, Antagonist | ||
| Kit Components |
| ||
| Shelf Life | 6 months | ||
| Orthologs Available | No | ||
| Shipping Requirements | Dry Ice | ||
| Storage temperature | -80C |
Data
Target Background
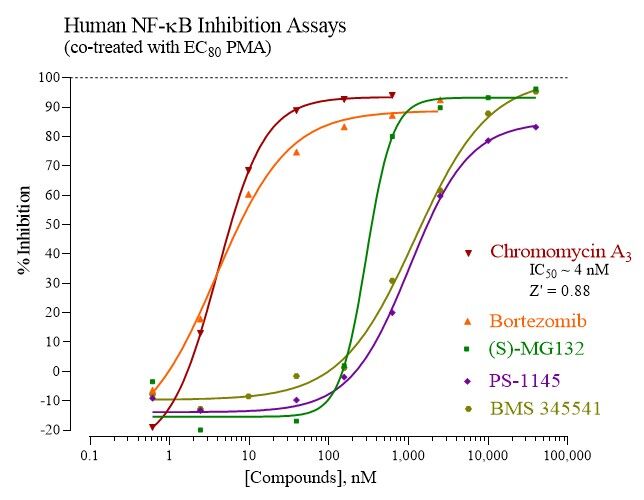
NF-kB is a signal transduction dependent transcription factor. INDIGO’s Human NF-kB Reporter Assay System utilizes proprietary human cells that express NF-kB (nuclear factor kappa-light-chain enhancer of activated B Cells), and contain the luciferase reporter gene functionally linked to upstream NF-kB genetic response elements. Thus, quantifying changes in luciferase expression provides a sensitive surrogate measure of changes in the level of NF-kB activation. This NF-kB reporter cell line is validated to provide a robust dose-dependent activation response when treated with TNFa, or the Protein Kinase C activator Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA). As such, the principle application of this assay system is in the screening of test samples to quantify any functional activities that they may exert to modulate, either induce or suppress, NF-kB activities.
Citations
Also available as a service